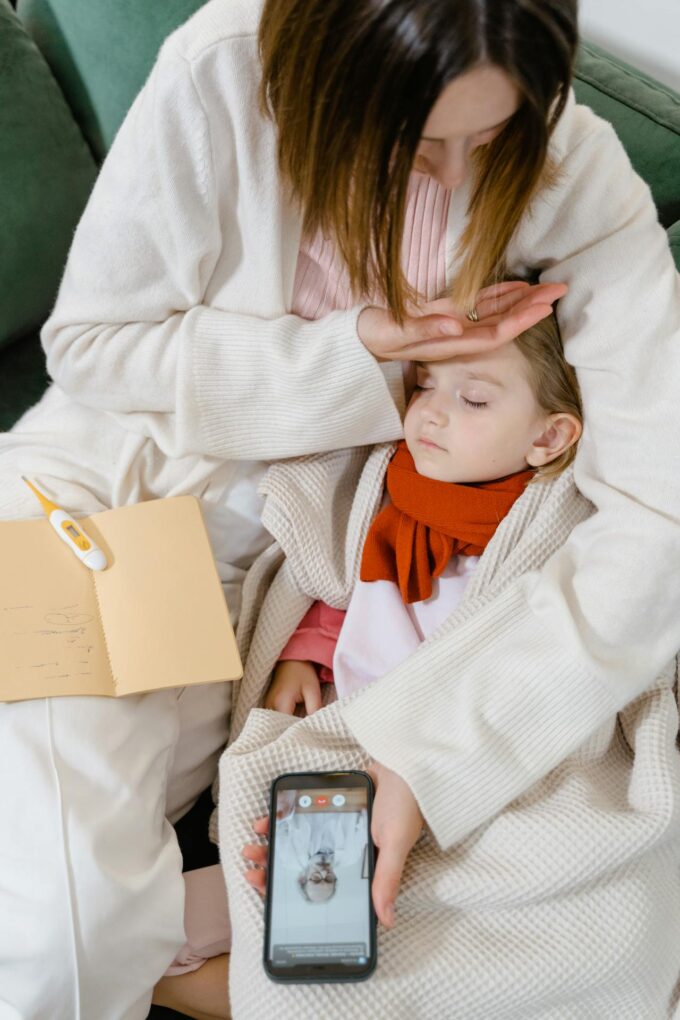
Photo by Tima Miroshnichenko
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the basics of telehealth and its integral role in healthcare.
- The advantages of telemedicine for both clinicians and patients.
- Challenges faced by the telehealth industry.
- How technology is driving telehealth forward.
- Predictions for the future of telehealth.
Table of Contents:
- What Is Telehealth?
- The Benefits of Telehealth
- Challenges in Telehealth
- Technological Advances Shaping Telehealth
- Telehealth in Practice: Real-World Applications
- The Patient Experience with Telehealth
- Ethical and Legal Considerations
- The Future of Telehealth
Telehealth revolutionizes modern healthcare delivery by leveraging electronic data and communication technologies to provide remote clinical services, public health administration, and health education. It enhances access to care, especially in underserved or rural areas, by connecting patients with healthcare professionals regardless of geographical barriers. Telehealth supports continuous patient monitoring, timely consultations, and efficient management of chronic conditions. It also reduces the need for in-person visits, lowering healthcare costs and minimizing exposure to infectious diseases. By integrating telehealth into healthcare systems, providers can improve the quality of care, patient outcomes, and overall healthcare efficiency.
What Is Telehealth?
Telehealth involves utilizing electronic data and communication technology to facilitate public health administration, provide professional and patient health education, and deliver clinical health care over long distances. Telehealth is a broad field, including telemedicine—clinical services—and other aspects like tele-education and telemonitoring. Institutions often collaborate with a telehealth solution provider with the required technological infrastructure to effectively implement these services.
The Benefits of Telehealth
Making healthcare more accessible is one of telehealth’s most significant benefits, particularly in underdeveloped and rural areas with limited access to medical treatment. It reduces the time and financial cost associated with traveling to receive care. For healthcare systems, it can lighten caseloads for busy in-person clinics and reduce the likelihood of patients spreading or contracting infectious diseases within a healthcare setting. Patient engagement and management also improve as patients use electronic prescriptions and online appointment scheduling services.
Challenges in Telehealth
Despite the promising landscape of telehealth, significant barriers hinder its widespread adoption. Access to necessary technology remains a primary obstacle, as not all patients possess smartphones or reliable internet connectivity. Even for those who do, navigating non-intuitive or inaccessible user interfaces can be challenging, particularly for older adults or individuals who are not technologically savvy. Additionally, reimbursement for telehealth services is a complex issue. Policies and regulations vary widely by insurer and state, creating a patchwork system that can limit the scope and consistency of telehealth’s reach. This variability in reimbursement can deter healthcare providers from offering telehealth services and restrict patients’ access to remote care. Overcoming these barriers is crucial for telehealth to achieve its full potential in enhancing healthcare accessibility and efficiency.
Technological Advances Shaping Telehealth
Continual technological advancements are shaping the future of telehealth. The widespread availability of high-speed internet has bolstered the reliability of video consultations, facilitating seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers. Smartphone apps have evolved to offer sophisticated health and wellness monitoring capabilities, providing users with actionable insights and promoting proactive self-care. Additionally, integrating AI and machine learning algorithms into patient triage and diagnostic systems is a fascinating growth area. These advancements make healthcare more proactive and personalized, allowing for early detection of health issues and tailored treatment plans. As technology advances, telehealth is poised to play an increasingly integral role in modern healthcare delivery, offering accessible, efficient, and personalized care to patients worldwide.
Telehealth in Practice: Real-World Applications
Practical applications of telehealth are diverse and impact virtually every aspect of healthcare. Mental health services, for example, have been revolutionized by the possibility of conducting therapy sessions through video conferencing. It’s not only the homebound who benefit; working professionals and students who struggle to fit appointments into their schedules can use telehealth as a flexible alternative. In chronic disease management, continuous monitoring via connected devices can help ensure patients follow treatment plans and allow for rapid response to any problematic changes in their condition.
The Patient Experience with Telehealth
Telehealth marks a profound transformation in the patient experience, empowering individuals with greater control over their health and well-being. Through telehealth, a mother can easily consult a pediatrician via video call in the middle of the night, a busy professional can conveniently renew a prescription during a lunch break, and a senior citizen can have a follow-up appointment without the hassle of arranging transportation. This unprecedented level of convenience not only enhances accessibility to healthcare but also fosters increased patient satisfaction. Such convenience aligns with the healthcare industry’s shift towards patient-centered care, where patient experience and satisfaction play pivotal roles. By prioritizing patient convenience and accessibility through telehealth, healthcare providers can deliver more personalized, timely, and convenient care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and overall satisfaction.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Data privacy and security are paramount because healthcare providers deal with sensitive patient information. Telehealth must comply with health data protection regulations such as HIPAA in the United States, necessitating robust security measures. In addition to data protection, telehealth services must consider equity in access to care. Disparities in internet access or technological literacy can exclude specific populations, raising concerns about whether telehealth is compounding instead of alleviating healthcare inequities. This calls for thoughtful approaches and policies that prioritize accessibility and inclusivity.
The Future of Telehealth
The future is bright for telehealth as it is a staple in healthcare delivery. The usage of telehealth services surged during the pandemic, proving that they can function as a primary healthcare delivery means. As the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports, telehealth has the potential to augment services in countless healthcare settings. With the continued enhancement, we expect telehealth to evolve into a fully integrated component of healthcare systems. Experts forecast that telehealth will become even more seamless and integrated with thoughtful regulation and continued technological innovation, paving the way toward a more efficient, effective, patient-centered healthcare system.